Electric vehicles (EVs) are no longer just the cars of the future, they are rapidly becoming a major part of our everyday lives. More drivers in the U.S. are making the switch to EVs, contributing to a reduction in pollution and enjoying significant savings on fuel costs. One of the primary factors driving this shift is the decreasing cost and increasing convenience of EVs. Thanks to government incentives and tax credits, buying an electric vehicle is now more affordable, while the expansion of charging infrastructure is making EVs easier to use than ever before. Leading automakers like Tesla, Ford, and General Motors are accelerating the EV race, offering a wide range of models that cater to different needs, from family-friendly cars to high-performance trucks.
As the electric car market continues to grow, it’s not just about saving money at the pump. EVs provide a quieter, smoother driving experience, require less maintenance, and offer significant environmental benefits. With advancements in technology, the range of electric vehicles is expanding, allowing drivers to travel farther on a single charge, while charging times are also getting faster. In the coming years, owning an EV will likely become just as common as driving a traditional gas-powered vehicle. This article will dive into the latest trends in EV growth in the U.S., highlighting the factors driving this surge and what the future holds for the electric vehicle market.
The Future of Electric Vehicles
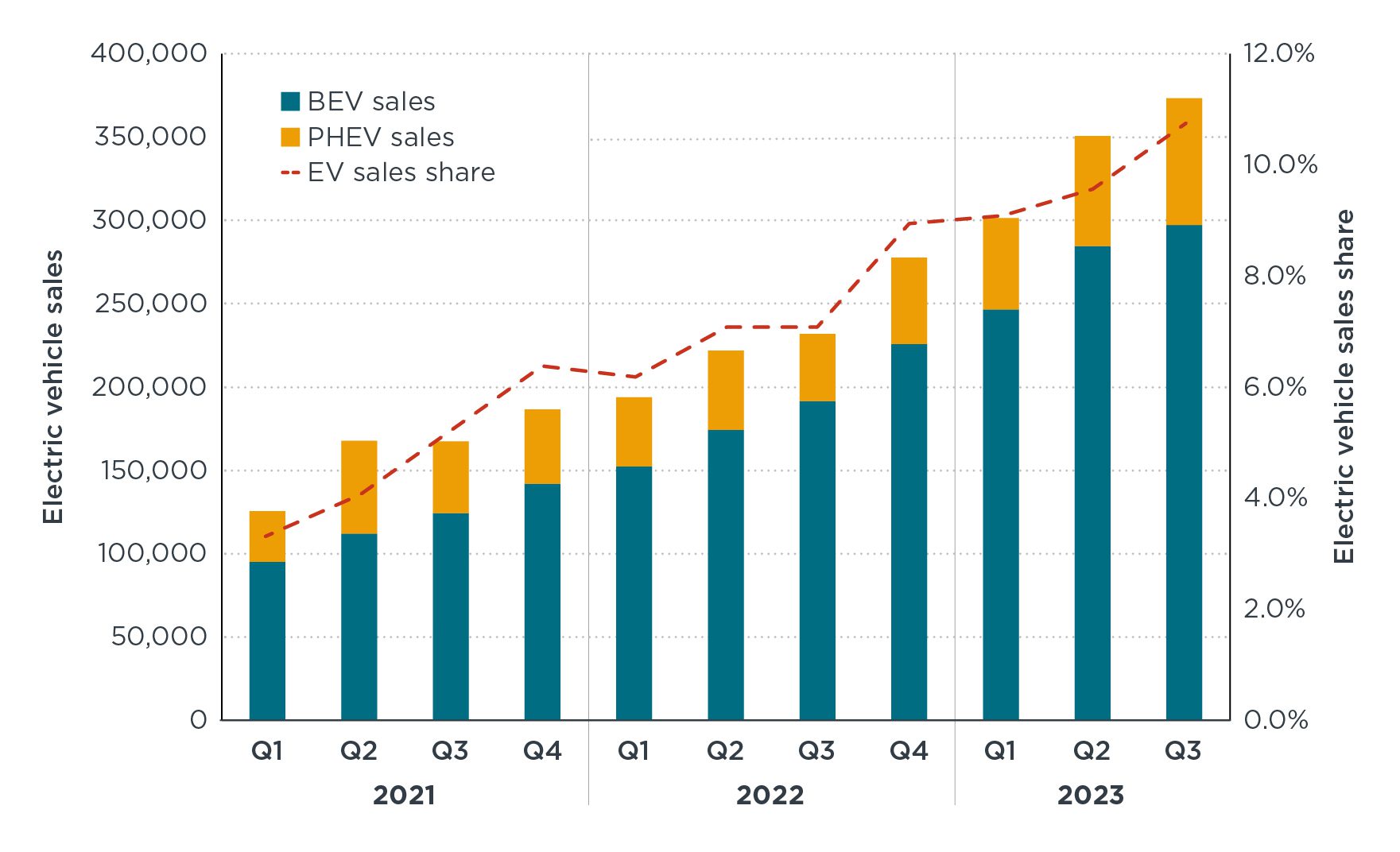
Electric vehicles (EVs) are poised to transform the transportation industry in the United States, driven by rapid advancements in battery technology, increased consumer awareness, and strong government support. Over the past decade, the EV market has grown exponentially, with sales in the U.S. increasing by over 500% since 2016. As the country seeks to reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainable energy, the rise of EVs represents a critical step in the shift towards cleaner transportation. In fact, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA), EV sales in the U.S. accounted for 7% of total vehicle sales in 2022, a significant leap from just 2.5% in 2020. This shift signals the beginning of a new era where electric vehicles may dominate the American automotive landscape within the next decade.

EV manufacturers are responding to increasing demand with a broader variety of models, from compact cars to luxury SUVs and electric trucks, designed to meet the diverse needs of U.S. consumers. Furthermore, advancements in battery technology are improving driving range, making EVs more practical for everyday use. With the U.S. being the world’s third-largest market for EVs, the stage is set for even more remarkable growth in the coming years as consumers shift away from gasoline-powered cars and towards electric alternatives.
1. Government Policies and Incentives Fueling Growth : The Future of Electric Vehicles
Federal and state governments in the U.S. have played a crucial role in encouraging the widespread adoption of electric vehicles by offering generous incentives and implementing policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions. The Biden administration has committed $7.5 billion to develop a national EV charging network, which aims to have 500,000 charging stations installed by 2030. This extensive infrastructure plan is vital for eliminating “range anxiety,” one of the key concerns potential EV buyers have about the availability of charging stations, particularly for long-distance travel.
Additionally, federal tax credits of up to $7,500 are available for new EV purchases, with some states offering additional incentives on top of this. For example, California, a leader in EV adoption, offers rebates up to $4,500 under its Clean Vehicle Rebate Project (CVRP). Furthermore, the state has set ambitious goals to phase out gasoline-powered vehicle sales by 2035. Other states, such as New York and Colorado, are offering similar incentives, making it financially viable for consumers to switch to electric vehicles. These programs not only help offset the higher upfront costs of EVs but also demonstrate the U.S. government’s commitment to achieving its climate goals, including the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by 50-52% below 2005 levels by 2030.
- California : Committed to banning the sale of new gasoline-powered vehicles by 2035.
- New York : Offering rebates up to $2,000 for EV buyers through its Drive Clean Rebate program.
- Colorado : Provides a state tax credit of $2,500 for purchasing an electric vehicle.
2. Expanding Model Variety and Consumer Choice : The Future of Electric Vehicles
The U.S. market for electric vehicles has grown beyond just niche models. Where EV options were once limited, the market now offers a diverse array of choices across various price points, vehicle types, and performance specifications. While Tesla remains the dominant player, with its Model 3 and Model Y being among the best-selling electric cars, traditional automakers like Ford, General Motors (GM), and Volkswagen have also made significant strides. Ford’s introduction of the F-150 Lightning, an electric version of its popular F-series truck, signals a critical shift in the perception of EVs as not just small, urban cars, but versatile, powerful vehicles that meet the broader demands of American consumers. The F-150 Lightning has already proven popular, with over 15,000 units sold in its first year of production.
Meanwhile, GM is positioning itself to be a leader in the EV space by pledging to release 30 new electric models by 2025 and to stop selling gas-powered vehicles altogether by 2035. On the luxury end of the market, brands like Porsche and Lucid Motors are offering high-performance EVs with industry-leading driving ranges and cutting-edge technology. This expansion of options has not only made electric vehicles more accessible to a wider range of consumers but has also encouraged more automakers to transition towards full electrification.
- Tesla / Tesla roadster : Sold over 1.3 million vehicles worldwide in 2022, dominating the EV market.
- Ford : Introduced the F-150 Lightning, selling over 15,000 units in its first year.
- General Motors : Plans to release 30 new electric models by 2025 and go fully electric by 2035.
3. Charging Infrastructure Development : The Future of Electric Vehicles
A critical factor in the success of EVs in the U.S. is the development of a reliable and widespread charging infrastructure. As of 2023, the U.S. had over 130,000 public charging points, but with the projected rise in EV sales, the demand for charging stations is set to increase dramatically. The Biden administration’s infrastructure bill, which allocates billions to EV charging stations, is designed to meet this growing need. Fast charging stations, in particular, are key to reducing charging times, making EVs more convenient for long trips. Companies like Tesla / Tesla roadster and Electrify America are leading the way in expanding this infrastructure, with Tesla’s Supercharger Network currently boasting over 1,400 stations across the U.S. and Electrify America planning to install 1,800 charging stations by 2026.
Private investments in EV charging infrastructure are also growing, with companies in the retail and hospitality sectors increasingly adding charging points to attract eco-conscious consumers. States such as Texas are taking the initiative by committing to build 2,000 EV charging stations as part of their highway infrastructure projects. These developments ensure that charging an EV will become as convenient as refueling a gasoline-powered vehicle, reducing one of the key barriers to mass EV adoption.
- Electrify America : Plans to install 1,800 charging stations by 2026.
- Tesla’s Supercharger Network : Over 1,400 stations across the U.S., providing fast and convenient charging for Tesla owners.
- Texas : Committed to building 2,000 EV charging stations as part of its highway infrastructure initiative.
4. Battery Technology Breakthroughs : The Future of Electric Vehicles
At the heart of every electric vehicle is its battery, and advancements in battery technology are essential for improving the performance, range, and affordability of EVs. Over the past decade, the cost of lithium-ion batteries has dropped by nearly 90%, making electric vehicles more competitive with traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. In the near future, solid-state batteries, which have 2-3 times the energy density of current lithium-ion batteries, could be a game-changer for the industry. These batteries promise to extend the driving range of EVs while reducing charging times significantly, addressing two of the main concerns among potential buyers.
Read also : Best Toronto Startups to Watch in 2024
Companies like QuantumScape and Toyota are at the forefront of developing this technology, with the first commercially available solid-state batteries expected to hit the market by 2025. Meanwhile, Tesla has made significant strides in reducing battery costs with its innovative 4680 battery cells, which are expected to lower production costs by 56%. These breakthroughs are not only making electric vehicles more affordable but also pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in terms of range and performance.
- Battery cost : Decreased by 89% in the last decade, now costing around $137 per kWh.
- Tesla / Tesla roadster : Plans to reduce battery costs by 56% with its 4680 battery cells.
- QuantumScape : Announced that its solid-state batteries could increase vehicle range by up to 80%.
5. Autonomous Driving and Electric Vehicles : The Future of Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles are also leading the charge when it comes to the development of autonomous driving technologies. Companies like Tesla roadster, Waymo, and Cruise are at the forefront of integrating self-driving capabilities into electric vehicles, which could drastically change the way Americans view car ownership and transportation. Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (FSD) software is already available for testing, and though it is currently in beta, the company plans to make it widely available by 2025. Waymo, the self-driving division of Alphabet, operates a fleet of fully autonomous taxis in Phoenix, Arizona, with plans to expand to more U.S. cities.
These advancements are expected to lead to a future where electric vehicles are not only the norm but are also capable of driving themselves, providing a safer, more efficient means of transportation. The rise of autonomous EVs could also reduce traffic congestion and lower the costs associated with car ownership, as shared autonomous electric vehicles become more widespread.
- Tesla FSD / Tesla roadster : Currently available for testing in beta mode, with widespread rollout expected by 2025.
- Waymo : Operates a fully autonomous taxi service in Phoenix, Arizona.
- Cruise : Expanded its self-driving EV service in San Francisco with plans to roll out nationwide.
6. Impact on Energy and the Grid : The Future of Electric Vehicles
The rapid growth of electric vehicle (EV) adoption in the United States poses significant challenges and opportunities for the nation’s energy grid. As more EVs hit the roads, the demand for electricity will rise sharply, placing increased pressure on an already strained grid. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, by 2030, EVs could account for up to 20% of total electricity consumption during peak hours in certain regions. This surge in demand could lead to grid instability and power shortages, especially in states like California and Texas, which have already experienced issues due to increased electricity use and climate-related stresses.
Technologies like Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) allow EVs to send unused electricity back to the grid during times of high demand. This would turn EVs into mobile energy storage units, helping to balance the supply and demand of electricity. For example, in California, where blackouts have become more common due to climate-driven heatwaves, V2G could help mitigate power shortages. In fact, experts predict that by 2030, V2G technology could provide enough power to supply over 5 million homes during peak demand periods.
Moreover, the integration of smart charging systems offers another solution. These systems enable EV owners to charge their vehicles during off-peak hours when electricity demand is lower, thereby reducing the strain on the grid. By encouraging off-peak charging and utilizing renewable energy sources, the U.S. can ensure that the growing EV market does not compromise the stability of its energy infrastructure.
- Electric Vehicles and Peak Electricity Use : EVs could account for 20% of electricity demand during peak hours by 2030.
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) : Technology could help stabilize the grid by supplying enough energy to power 5 million homes by 2030.
- Smart Grids : Digital systems to manage energy flow and reduce grid strain caused by increased EV adoption.
Challenges of the EV Market
Lack of Charging Stations
One of the biggest issues is the limited number of charging stations, especially in rural areas. While cities have more chargers, smaller towns and less populated states often don’t have enough. As of 2023, there are over 150,000 charging stations across the country, but this number is still far from meeting the needs of the growing number of EVs. By 2030, it’s expected that 26 million EVs will be on U.S. roads, and without more charging options, many drivers may worry about running out of power.
High Cost of EVs
Electric vehicles can be expensive. The average price of an EV in 2023 is about $53,000, which is higher than the $48,000 average price of traditional cars. While there are federal tax credits of up to $7,500 and state incentives to help, many buyers still find EVs too pricey.
Supply Chain Issues
The production of EVs has been slowed by supply chain problems, especially for batteries. EV batteries rely on materials like lithium and cobalt, which are mostly imported. This makes the U.S. dependent on other countries for key parts, which can cause delays and price increases.
Consumer Hesitation
Many U.S. consumers are still unsure about switching to electric vehicles. Some worry about battery life, charging convenience, and how long an EV will last. While about 60% of Americans say they are interested in EVs, many still don’t know enough about them or feel there aren’t enough incentives to make the switch.
Battery Recycling Concerns
While EVs are better for the environment in terms of emissions, disposing of old batteries can be harmful if not done correctly. Currently, only a small portion of EV batteries are being recycled. As more EVs reach the end of their life, the U.S. will need to improve its battery recycling systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the future of electric vehicles (EVs) in the United States looks promising, but there are still challenges to overcome. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect significant improvements in EV affordability, charging infrastructure, and battery efficiency. This will make EVs more accessible to a wider range of consumers. Moreover, the U.S. government’s commitment to clean energy and the growing demand for eco-friendly transportation will further drive EV adoption.
However, it’s important to address the existing concerns, such as the need for more charging stations and reliable battery recycling programs. By tackling these issues, the U.S. can strengthen its leadership in the global EV market and contribute to a more sustainable future. As automakers, policymakers, and consumers work together, the road ahead for electric vehicles in the U.S. is set to become smoother and more electrifying.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the future of electric cars in 2030?
By 2030, the future of electric cars looks bright, with rapid advancements in technology and increasing adoption worldwide. In the U.S., electric vehicles (EVs) are expected to make up a significant portion of new car sales, driven by improvements in battery efficiency, longer driving ranges, and faster charging times.
Will electric vehicles be successful?
Yes, Electric vehicles (EVs) are poised for success due to several key factors. As technology continues to improve, EVs are becoming more affordable, efficient, and practical for everyday use. Government incentives, growing environmental awareness, and advances in charging infrastructure are all contributing to their popularity.
Will hydrogen cars overtake EV?
Yes, several alternatives to electric cars are emerging. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles use hydrogen to generate electricity, emitting only water vapor as a byproduct. Biofuel-powered cars run on renewable fuels derived from organic materials, providing another sustainable option.
Will there be an alternative to electric cars?
Yes, Alternatives to electric cars exist and continue to develop. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles use hydrogen to generate electricity and emit only water vapor, offering a clean transportation option. Additionally, biofuel-powered cars run on renewable fuels derived from organic materials, providing another sustainable alternative.



